Kubernetes Letschat
Introduccion
Kubernetes se ha convertido en el estándar para la orquestación de contenedores. Si bien herramientas como Docker permiten ejecutar contenedores fácilmente, cuando tienes decenas (o cientos) de aplicaciones desplegadas, mantenerlas disponibles, escalarlas y actualizarlas manualmente se vuelve un reto.
Ahí es donde entra Kubernetes (K8s): una plataforma de código abierto diseñada para automatizar el despliegue, escalado y gestión de aplicaciones en contenedores.
En este post aprenderás los conceptos básicos de Kubernetes y montarás un pequeño clúster local con tres máquinas virtuales usando Vagrant y Ansible, sobre el que desplegarás tu primera aplicación: Let’s Chat, una app de mensajería autohospedada.
¿Qué es Kubernetes?
Kubernetes coordina contenedores en múltiples máquinas, gestionando su disponibilidad, escalado y comunicación.
Para entenderlo mejor, veamos sus elementos fundamentales:
| Concepto | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Clúster | Conjunto de máquinas (nodos) que actúan como un único sistema. |
| Nodo maestro (Control Plane) | Gestiona el estado del clúster, planifica los pods y responde a los comandos kubectl. |
| Nodos de trabajo (Workers) | Ejecutan las cargas de trabajo, es decir, los contenedores (pods). |
| Pod | Unidad mínima de ejecución en Kubernetes; puede contener uno o varios contenedores. |
| Deployment | Define cuántos pods debe haber y cómo deben actualizarse. |
| Service | Expone los pods dentro o fuera del clúster para que sean accesibles. |
En resumen: tú defines el estado deseado (por ejemplo, “quiero 3 copias de mi aplicación web”), y Kubernetes se encarga de mantenerlo automáticamente.
Requisitos previos
- Equipo con al menos 8 GB de RAM.
- Tener instalados Vagrant, VirtualBox y Ansible.
- Conocimientos básicos de Linux y SSH.
Preparacion del escenario
Empezamos creando en nuestro equipo un directorio donde almacenaremos nuestro escenario vagrant. Dicho escenario sera el siguiente:
# -*- mode: ruby -*-
# vi: set ft=ruby :
IMAGE_NAME = "bento/ubuntu-16.04"
N = 2
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.ssh.insert_key = false
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |v|
v.memory = 2048
v.cpus = 2
end
config.vm.define "k8s-master" do |master|
master.vm.box = IMAGE_NAME
master.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.50.10"
master.vm.hostname = "k8s-master"
master.vm.provision "ansible" do |ansible|
ansible.playbook = "kubernetes-setup/master-playbook.yml"
ansible.extra_vars = {
node_ip: "192.168.50.10",
}
end
end
(1..N).each do |i|
config.vm.define "node-#{i}" do |node|
node.vm.box = IMAGE_NAME
node.vm.network "private_network", ip: "192.168.50.#{i + 10}"
node.vm.hostname = "node-#{i}"
node.vm.provision "ansible" do |ansible|
ansible.playbook = "kubernetes-setup/node-playbook.yml"
ansible.extra_vars = {
node_ip: "192.168.50.#{i + 10}",
}
end
end
end
end
Con este escenario desplegaremos 3 maquinas, una maquina master en la que se instalara ansible y ejecutara el playbook que pondremos, y 2 nodos en los que se ejecutara ansible también pero con un playbook distinto.
Para que el despliegue mas adelante funcione, sera necesario tener instalado en la maquina anfitriona ansible, en mi caso la version 2.7.7, ya que es el ansible de la maquina anfitriona el que se instalara posteriormente en las maquinas de nuestro escenario.
Los dos playbooks los crearemos en un directorio dentro de nuestro directorio de kubernetes con el siguiente contenido:
master-playbook.yaml:
- hosts: all
become: true
tasks:
- name: Instala los paquetes que permite usar APT con HTTPS
apt:
name: ""
state: present
update_cache: yes
vars:
packages:
- apt-transport-https
- ca-certificates
- curl
- gnupg-agent
- software-properties-common
- name: Añade la clave apt para Docker
apt_key:
url: https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg
state: present
- name: Añade el repositorio apt de la versión estable
apt_repository:
repo: deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu xenial stable
state: present
- name: Instala Docker y sus dependencias
apt:
name: ""
state: present
update_cache: yes
vars:
packages:
- docker-ce
- docker-ce-cli
- containerd.io
notify:
- docker status
- name: Añade al usuario vagrant al grupo de docker
user:
name: vagrant
group: docker
- name: Elimina el fichero swap de /etc/fstab
mount:
name: ""
fstype: swap
state: absent
with_items:
- swap
- none
- name: Deshabilita el swap
command: swapoff -a
when: ansible_swaptotal_mb > 0
- name: Añade la clave apt para Kubernetes
apt_key:
url: https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg
state: present
- name: Añade el repositorio apt para Kubernetes
apt_repository:
repo: deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main
state: present
filename: kubernetes.list
- name: Instala los binarios de Kubernetes
apt:
name: ""
state: present
update_cache: yes
vars:
packages:
- kubelet
- kubeadm
- kubectl
- name: Configura el node ip
lineinfile:
path: /etc/default/kubelet
line: KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS=--node-ip=
create: yes
- name: Reinicia kubelet
service:
name: kubelet
daemon_reload: yes
state: restarted
- name: Reinicia Docker
systemd:
name: docker
state: restarted
- name: Inicializa el cluster de Kubernetes usando kubeadm
command: kubeadm init --apiserver-advertise-address="192.168.50.10" --apiserver-cert-extra-sans="192.168.50.10" --pod-network-cidr=192.168.0.0/16 --node-name k8s-master
- name: Organiza el kubeconfig del usuario vagrant
command: ""
with_items:
- mkdir -p /home/vagrant/.kube
- cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf /home/vagrant/.kube/config
- chown vagrant:vagrant /home/vagrant/.kube/config
- name: Instala el pod de red Calico
become: false
command: kubectl create -f https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/tigera-operator.yaml
- name: Instala el pod de red Calico 2
become: false
command: kubectl create -f https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/custom-resources.yaml
- name: Genera el comando de join
command: kubeadm token create --print-join-command
register: join_command
- name: Copia el comando de join a un fichero local
become: false
local_action: copy content="" dest="./join-command"
handlers:
- name: docker status
service: name=docker state=started
node-playbook.yaml:
- hosts: all
become: true
tasks:
- name: Instala los paquetes que permite usar APT con HTTPS
apt:
name: ""
state: present
update_cache: yes
vars:
packages:
- apt-transport-https
- ca-certificates
- curl
- gnupg-agent
- software-properties-common
- name: Añade la clave apt para Docker
apt_key:
url: https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg
state: present
- name: Añade el repositorio apt de la versión estable
apt_repository:
repo: deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu xenial stable
state: present
- name: Instala Docker y sus dependencias
apt:
name: ""
state: present
update_cache: yes
vars:
packages:
- docker-ce
- docker-ce-cli
- containerd.io
notify:
- docker status
- name: Añade al usuario vagrant al grupo de Docker
user:
name: vagrant
group: docker
- name: Elimina el fichero de swap de /etc/fstab
mount:
name: ""
fstype: swap
state: absent
with_items:
- swap
- none
- name: Deshabilita el swap
command: swapoff -a
when: ansible_swaptotal_mb > 0
- name: Añade la clave apt para Kubernetes
apt_key:
url: https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg
state: present
- name: Añade el repositorio apt para Kubernetes
apt_repository:
repo: deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main
state: present
filename: kubernetes.list
- name: Instala los binarios para Kubernetes
apt:
name: ""
state: present
update_cache: yes
vars:
packages:
- kubelet
- kubeadm
- kubectl
- name: Configura node ip
lineinfile:
path: /etc/default/kubelet
line: KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS=--node-ip=
create: yes
- name: Reinicia kubelet
service:
name: kubelet
daemon_reload: yes
state: restarted
- name: Reinicia Docker
systemd:
name: docker
state: restarted
- name: Copia el comando de join a la localización del server
copy: src=join-command dest=/tmp/join-command.sh mode=0777
- name: Une el nodo al clúster
command: sh /tmp/join-command.sh
handlers:
- name: docker status
service: name=docker state=started
Levantamos el escenario:
sergioib@debian-sergio:~/Escritorio/Informatica/Vagrant/k8$ vagrant up
Bringing machine 'k8s-master' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
Bringing machine 'node-1' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
Bringing machine 'node-2' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
==> k8s-master: Importing base box 'bento/ubuntu-16.04'...
==> k8s-master: Matching MAC address for NAT networking...
==> k8s-master: Checking if box 'bento/ubuntu-16.04' version '202102.02.0' is up to date...
==> k8s-master: Setting the name of the VM: k8_k8s-master_1615035261709_29283
==> k8s-master: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> k8s-master: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
k8s-master: Adapter 1: nat
k8s-master: Adapter 2: hostonly
==> k8s-master: Forwarding ports...
k8s-master: 22 (guest) => 2222 (host) (adapter 1)
==> k8s-master: Running 'pre-boot' VM customizations...
==> k8s-master: Booting VM...
==> k8s-master: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes...
k8s-master: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2222
k8s-master: SSH username: vagrant
k8s-master: SSH auth method: private key
==> k8s-master: Machine booted and ready!
==> k8s-master: Checking for guest additions in VM...
k8s-master: The guest additions on this VM do not match the installed version of
k8s-master: VirtualBox! In most cases this is fine, but in rare cases it can
k8s-master: prevent things such as shared folders from working properly. If you see
k8s-master: shared folder errors, please make sure the guest additions within the
k8s-master: virtual machine match the version of VirtualBox you have installed on
k8s-master: your host and reload your VM.
k8s-master:
k8s-master: Guest Additions Version: 6.1.18
k8s-master: VirtualBox Version: 6.0
==> k8s-master: Setting hostname...
==> k8s-master: Configuring and enabling network interfaces...
==> k8s-master: Mounting shared folders...
k8s-master: /vagrant => /home/sergioib/Escritorio/Informatica/Vagrant/k8
==> k8s-master: Running provisioner: ansible...
Vagrant has automatically selected the compatibility mode '2.0'
according to the Ansible version installed (2.7.7).
Alternatively, the compatibility mode can be specified in your Vagrantfile:
https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/provisioning/ansible_common.html#compatibility_mode
k8s-master: Running ansible-playbook...
PLAY [all] *********************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [k8s-master]
TASK [Instala los paquetes que permite usar APT con HTTPS] *********************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Añade la clave apt para Docker] ******************************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Añade el repositorio apt de la versión estable] **************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Instala Docker y sus dependencias] ***************************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Añade al usuario vagrant al grupo de docker] *****************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Elimina el fichero swap de /etc/fstab] ***********************************
ok: [k8s-master] => (item=swap)
changed: [k8s-master] => (item=none)
TASK [Deshabilita el swap] *****************************************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Añade la clave apt para Kubernetes] **************************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Añade el repositorio apt para Kubernetes] ********************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Instala los binarios de Kubernetes] **************************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Configura el node ip] ****************************************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Reinicia kubelet] ********************************************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Reinicia Docker] *********************************************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Inicializa el cluster de Kubernetes usando kubeadm] **********************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Organiza el kubeconfig del usuario vagrant] ******************************
changed: [k8s-master] => (item=mkdir -p /home/vagrant/.kube)
changed: [k8s-master] => (item=cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf /home/vagrant/.kube/config)
changed: [k8s-master] => (item=chown vagrant:vagrant /home/vagrant/.kube/config)
[WARNING]: Consider using the file module with state=directory rather than
running mkdir. If you need to use command because file is insufficient you can
add warn=False to this command task or set command_warnings=False in
ansible.cfg to get rid of this message.
[WARNING]: Consider using the file module with owner rather than running
chown. If you need to use command because file is insufficient you can add
warn=False to this command task or set command_warnings=False in ansible.cfg to
get rid of this message.
TASK [Instala el pod de red Calico] ********************************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Instala el pod de red Calico 2] ******************************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Genera el comando de join] ***********************************************
changed: [k8s-master]
TASK [Copia el comando de join a un fichero local] *****************************
changed: [k8s-master -> localhost]
RUNNING HANDLER [docker status] ************************************************
ok: [k8s-master]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
k8s-master : ok=21 changed=19 unreachable=0 failed=0
==> node-1: Importing base box 'bento/ubuntu-16.04'...
==> node-1: Matching MAC address for NAT networking...
==> node-1: Checking if box 'bento/ubuntu-16.04' version '202102.02.0' is up to date...
==> node-1: Setting the name of the VM: k8_node-1_1615035591709_14063
==> node-1: Fixed port collision for 22 => 2222. Now on port 2200.
==> node-1: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> node-1: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
node-1: Adapter 1: nat
node-1: Adapter 2: hostonly
==> node-1: Forwarding ports...
node-1: 22 (guest) => 2200 (host) (adapter 1)
==> node-1: Running 'pre-boot' VM customizations...
==> node-1: Booting VM...
==> node-1: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes...
node-1: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2200
node-1: SSH username: vagrant
node-1: SSH auth method: private key
==> node-1: Machine booted and ready!
==> node-1: Checking for guest additions in VM...
node-1: The guest additions on this VM do not match the installed version of
node-1: VirtualBox! In most cases this is fine, but in rare cases it can
node-1: prevent things such as shared folders from working properly. If you see
node-1: shared folder errors, please make sure the guest additions within the
node-1: virtual machine match the version of VirtualBox you have installed on
node-1: your host and reload your VM.
node-1:
node-1: Guest Additions Version: 6.1.18
node-1: VirtualBox Version: 6.0
==> node-1: Setting hostname...
==> node-1: Configuring and enabling network interfaces...
==> node-1: Mounting shared folders...
node-1: /vagrant => /home/sergioib/Escritorio/Informatica/Vagrant/k8
==> node-1: Running provisioner: ansible...
Vagrant has automatically selected the compatibility mode '2.0'
according to the Ansible version installed (2.7.7).
Alternatively, the compatibility mode can be specified in your Vagrantfile:
https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/provisioning/ansible_common.html#compatibility_mode
node-1: Running ansible-playbook...
PLAY [all] *********************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [node-1]
TASK [Instala los paquetes que permite usar APT con HTTPS] *********************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Añade la clave apt para Docker] ******************************************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Añade el repositorio apt de la versión estable] **************************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Instala Docker y sus dependencias] ***************************************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Añade al usuario vagrant al grupo de Docker] *****************************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Elimina el fichero de swap de /etc/fstab] ********************************
ok: [node-1] => (item=swap)
changed: [node-1] => (item=none)
TASK [Deshabilita el swap] *****************************************************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Añade la clave apt para Kubernetes] **************************************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Añade el repositorio apt para Kubernetes] ********************************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Instala los binarios para Kubernetes] ************************************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Configura node ip] *******************************************************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Reinicia kubelet] ********************************************************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Reinicia Docker] *********************************************************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Copia el comando de join a la localización del server] *******************
changed: [node-1]
TASK [Une el nodo al clúster] **************************************************
changed: [node-1]
RUNNING HANDLER [docker status] ************************************************
ok: [node-1]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
node-1 : ok=17 changed=15 unreachable=0 failed=0
==> node-2: Importing base box 'bento/ubuntu-16.04'...
==> node-2: Matching MAC address for NAT networking...
==> node-2: Checking if box 'bento/ubuntu-16.04' version '202102.02.0' is up to date...
==> node-2: Setting the name of the VM: k8_node-2_1615035854760_61331
==> node-2: Fixed port collision for 22 => 2222. Now on port 2201.
==> node-2: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> node-2: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
node-2: Adapter 1: nat
node-2: Adapter 2: hostonly
==> node-2: Forwarding ports...
node-2: 22 (guest) => 2201 (host) (adapter 1)
==> node-2: Running 'pre-boot' VM customizations...
==> node-2: Booting VM...
==> node-2: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes...
node-2: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2201
node-2: SSH username: vagrant
node-2: SSH auth method: private key
==> node-2: Machine booted and ready!
==> node-2: Checking for guest additions in VM...
node-2: The guest additions on this VM do not match the installed version of
node-2: VirtualBox! In most cases this is fine, but in rare cases it can
node-2: prevent things such as shared folders from working properly. If you see
node-2: shared folder errors, please make sure the guest additions within the
node-2: virtual machine match the version of VirtualBox you have installed on
node-2: your host and reload your VM.
node-2:
node-2: Guest Additions Version: 6.1.18
node-2: VirtualBox Version: 6.0
==> node-2: Setting hostname...
==> node-2: Configuring and enabling network interfaces...
==> node-2: Mounting shared folders...
node-2: /vagrant => /home/sergioib/Escritorio/Informatica/Vagrant/k8
==> node-2: Running provisioner: ansible...
Vagrant has automatically selected the compatibility mode '2.0'
according to the Ansible version installed (2.7.7).
Alternatively, the compatibility mode can be specified in your Vagrantfile:
https://www.vagrantup.com/docs/provisioning/ansible_common.html#compatibility_mode
node-2: Running ansible-playbook...
PLAY [all] *********************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [node-2]
TASK [Instala los paquetes que permite usar APT con HTTPS] *********************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Añade la clave apt para Docker] ******************************************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Añade el repositorio apt de la versión estable] **************************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Instala Docker y sus dependencias] ***************************************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Añade al usuario vagrant al grupo de Docker] *****************************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Elimina el fichero de swap de /etc/fstab] ********************************
ok: [node-2] => (item=swap)
changed: [node-2] => (item=none)
TASK [Deshabilita el swap] *****************************************************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Añade la clave apt para Kubernetes] **************************************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Añade el repositorio apt para Kubernetes] ********************************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Instala los binarios para Kubernetes] ************************************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Configura node ip] *******************************************************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Reinicia kubelet] ********************************************************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Reinicia Docker] *********************************************************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Copia el comando de join a la localización del server] *******************
changed: [node-2]
TASK [Une el nodo al clúster] **************************************************
changed: [node-2]
RUNNING HANDLER [docker status] ************************************************
ok: [node-2]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
node-2 : ok=17 changed=15 unreachable=0 failed=0
Accedemos a nuestra maquina master para comprobar que a este se le han unido los dos nodos si el despliegue a ido correctamente.
vagrant@k8s-master:~$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master Ready control-plane,master 19m v1.20.4
node-1 NotReady <none> 15m v1.20.4
node-2 NotReady <none> 10m v1.20.4
Para poder acceder desde nuestra maquina en lugar de desde nuestro master, copiamos el contenido de .kube/config y lo copiamos en el .kube/config en nuestra maquina anfitriona y comprobamos que podemos ejecutar los comandos en nuestra maquina.
sergioib@debian-sergio:~$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master Ready control-plane,master 26m v1.20.4
node-1 Ready <none> 22m v1.20.4
node-2 Ready <none> 17m v1.20.4
Copiamos los ficheros donde tenemos los ficheros para el despliegue de letschat en nuestro directorio kubernetes-setup y los añadimos al escenario de la siguiente forma:
sergioib@debian-sergio:~/Escritorio/Informatica/Vagrant/k8/kubernetes-setup$ kubectl create -f mongo-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/mongo created
sergioib@debian-sergio:~/Escritorio/Informatica/Vagrant/k8/kubernetes-setup$ kubectl create -f mongo-srv.yaml
service/mongo created
sergioib@debian-sergio:~/Escritorio/Informatica/Vagrant/k8/kubernetes-setup$ kubectl create -f letschat-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/letschat created
sergioib@debian-sergio:~/Escritorio/Informatica/Vagrant/k8/kubernetes-setup$ kubectl create -f letschat-srv.yaml
service/letschat created
Comprobamos que funcione, para ello ejecutamos o bien un kubectl get service o bien un kubectl get all para saber en que puerto se esta ejecutando nuestro letschat y una vez sepamos el puerto comprobamos que se esta ejecutando en el navegador.
sergioib@debian-sergio:~$ kubectl get service
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 26h
letschat NodePort 10.99.77.113 <none> 8080:30961/TCP 25h
mongo ClusterIP 10.103.65.204 <none> 27017/TCP 26h
sergioib@debian-sergio:~$ kubectl get all
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/letschat-7c66bd64f5-w2frt 0/1 Error 19 26h
pod/mongo-5c694c878b-flgcg 0/1 Error 10 26h
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 26h
service/letschat NodePort 10.99.77.113 <none> 8080:30961/TCP 25h
service/mongo ClusterIP 10.103.65.204 <none> 27017/TCP 26h
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/letschat 1/1 1 1 26h
deployment.apps/mongo 1/1 1 1 26h
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/letschat-7c66bd64f5 1 1 1 26h
replicaset.apps/mongo-5c694c878b 1 1 1 26h
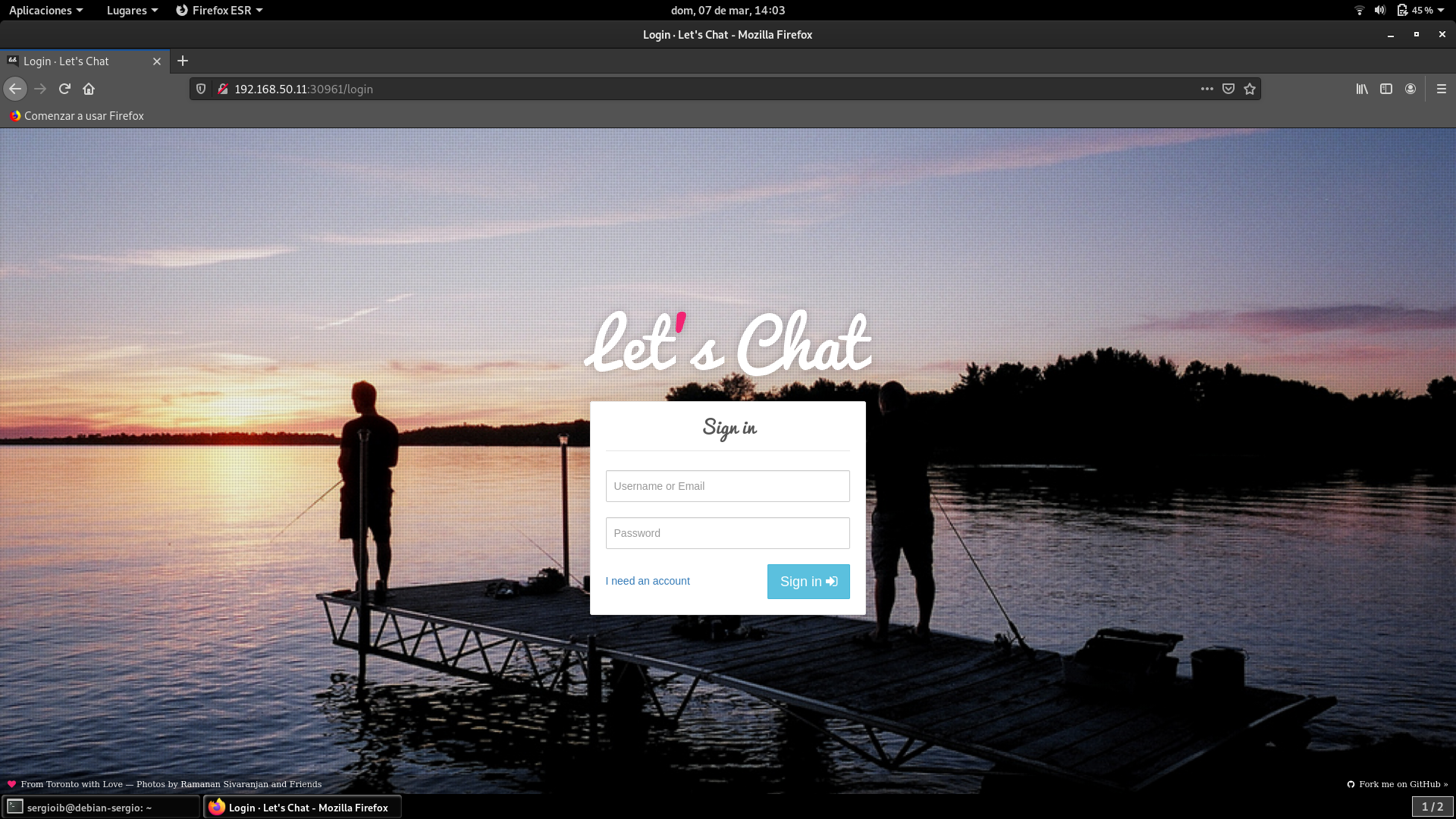
Una vez que se haya comprobado que funcione, probamos a escalar varias replicas de la siguiente forma:
sergioib@debian-sergio:~$ kubectl scale --replicas=3 deploy/letschat
deployment.apps/letschat scaled
Comprobamos que se hayan creado dos pods nuevos:
sergioib@debian-sergio:~$ kubectl get pod -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
letschat-7c66bd64f5-75kjv 1/1 Running 2 46m 192.168.84.147 node-1 <none> <none>
letschat-7c66bd64f5-zbbn7 1/1 Running 7 46m 192.168.247.23 node-2 <none> <none>
letschat-7c66bd64f5-zc5k7 1/1 Running 1 20m 192.168.247.22 node-2 <none> <none>
mongo-5c694c878b-flgcg 1/1 Running 14 27h 192.168.84.148 node-1 <none> <none>
Como se puede ver se ha creado un nuevo pod. al indicar que haya 3 replicas como en este ejemplo, en el caso de eliminar una de las replicas se creara otro de forma automática. En el caso de tener varias replicas activadas, al hacer una desescalada el nodo que permanecerá sera el de mayor antigüedad.
Conclusión
Has creado tu primer clúster de Kubernetes local y desplegado una aplicación real. En el proceso, aprendiste:
-
Qué es un clúster, nodo, pod, deployment y service.
-
Cómo usar Ansible para automatizar la instalación de Kubernetes.
-
Cómo desplegar, escalar y exponer una aplicación.
Esto sienta una base sólida para avanzar hacia temas más avanzados como:
-
Helm (gestor de paquetes para Kubernetes)
-
Ingress (rutas HTTP internas/externas)
-
Volúmenes persistentes y almacenamiento
-
Monitorización con Prometheus y Grafana